Industry insights on skills needs
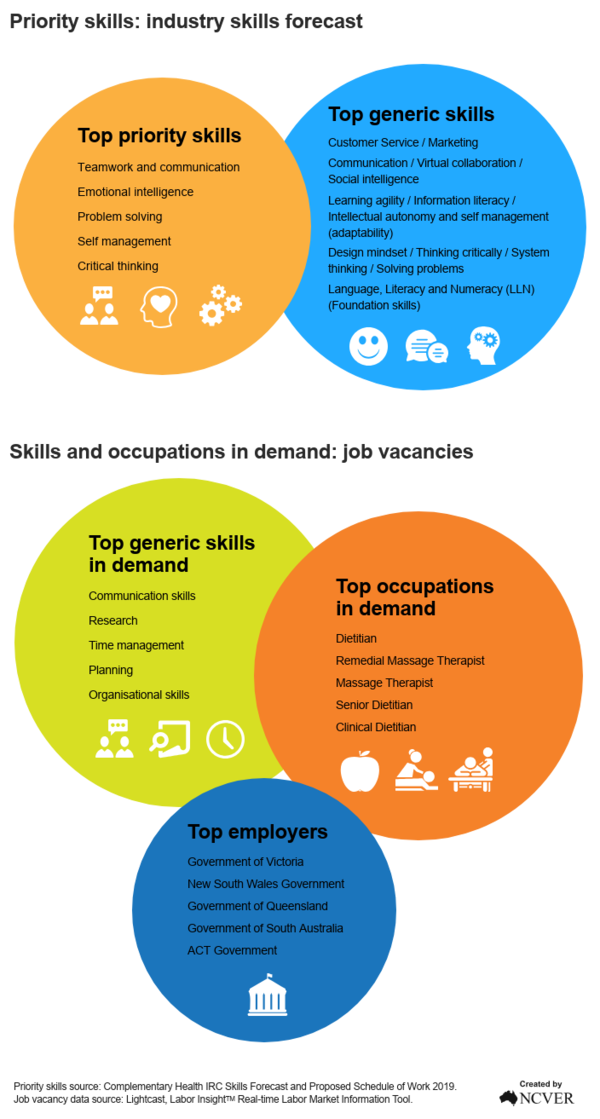
The Complementary Health IRC's 2019 Skills Forecast was the most recently published industry skills forecast by the IRC, as of September 2022. It identified the top priority skills for the sector as teamwork and communication, emotional intelligence, problem solving, self-management and critical thinking.
The top five identified generic skills are:
- Customer Service / Marketing
- Communication / Virtual collaboration / Social intelligence
- Learning agility / Information literacy / Intellectual autonomy and self-management (adaptability)
- Design mindset / Thinking critically / System thinking / Solving problems
- Language, Literacy and Numeracy (LLN) (Foundation skills).
According to the job vacancy data, the top requested skills by employers in the sector were communication skills and research. The most advertised occupations were Dietitian, followed by Remedial Massage Therapist. The top employers were the Government of Victoria and the New South Wales Government.
According to the Complementary Health IRC's 2019 Skills Forecast, over recent times treatment practices for Massage Therapists, as well as the wider Complementary Health professional workforce, have evolved significantly. Such change has resulted in evolving skill and competence requirements for the workforce.
The sector overall has been experiencing several challenges which are impacting workforce skill requirements including:
- Government policy/legislation affecting private health insurance rebates
- Ageing workforce and an ageing population
- Skills shortages
- Employment status and earnings.
Government policy/legislation
From April 2019, private health insurance providers no longer receive government subsidies for providing rebates across 12–16 natural therapies following the 2015 Review of the Australian Government Rebate on Private Health Insurance for Natural Therapies. Most of the therapies under the remit of the Complementary Health IRC were affected, including Ayurveda, Aromatherapy, Kinesiology, Shiatsu, Reflexology and TCM Remedial Massage. Remedial Massage Therapy was excluded from the change and continues to attract rebates.
The Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care announced the Natural Therapies Review 2019-20 in April 2019. The Review is assessing the clinical effectiveness of the 16 natural therapies excluded from private health insurance rebates from 1 April 2019 by looking at additional evidence. The National Health Medical Research Committee has established the Natural Therapies Working Committee to oversee the evidence by the end of December 2021, with a possibility of an extension. The Committee is expected to advisethe Government if private health insurance should cover any of the therapies.
Ageing workforce
The Complementary Health IRC's 2019 Skills Forecast reports the ageing trend of its workforce presents the challenge of adopting workplace arrangements that will retain a substantial level of mature-age workers. In some cases, over half (54%) of the workforce in some Complementary Health roles (e.g. Complementary Health Therapists) are aged 45 years and over (registering an average age of 47 years, compared to the all-job average of 40 years).
Proactively implementing measures, such as flexible working conditions to retain older, skilled workers, and other initiatives, such as succession planning for businesses and accessing a sufficiently skilled pool of graduates or new entrants is critical within a sector, which consists predominantly of small businesses.
Providing channels in the VET sector to gain higher-level and/or further skills (for example, via an Advanced Diploma and/or skill sets to extend the scope of practice) may provide older workers with further learning opportunities and younger workers with career pathways.
Skills shortages
Within the Complementary Health sector, skills shortages are seen to be contributing to insufficiently trained practitioners. The skills shortage partially stems from historically inconsistent training provided by educational institutions, resulting in varied levels of skills and abilities. In addition to the inadequate quality of training, there is also a scarce quantity of experienced teaching staff, with Registered Training Organisations (RTOs) at times resorting to recruiting newly graduated students for teaching positions. Additionally, Complementary Health Practitioners who have gained their qualification/s through Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) do not meet the educational criteria necessary to be recognised by certain health fund providers.
Due to these challenges, certain job roles in the Complementary Health sector, such as Complementary Health Therapist and Massage Therapist job roles, were listed under the Temporary Skills Shortage (TSS) visa's Short-Term Skills Occupation List – a list which specifies occupations for 482 visa and migration application. Addressing these skills gaps is necessary, principally due to the increasing level of demand from an ageing population, who supplement Complementary Health services as part of palliative care.
However, the Massage & Myotherapy submission (No.142) to the Inquiry into Australia’s Skilled Migration Program sought a change to the policy to ensure only appropriately skilled and trained therapists pass the skilled migration program, or removal of massage therapists from the skilled migration list.
Employment status and earnings
Research has found that most Complementary Health practitioners work part-time and some Complementary Health therapists doing body work can only do around 25 one-hour massages in a week and many do fewer. A workforce survey of 480 message therapists in 2017 revealed the majority are either self-employed sole traders (64%) or sub-contracting their services to other businesses (24%). Further, non-genuine contracting practices are common within the industry, which is reflected by the relatively small percentage of therapists who are employed under the Health Professionals and Support Services Award. A recent survey by the Shiatsu Therapy Association Australia (STAA) found the majority (75%) of Shiatsu Practitioners work part-time. Part-time employment has a flow-on effect on the level of potential earnings for workers.